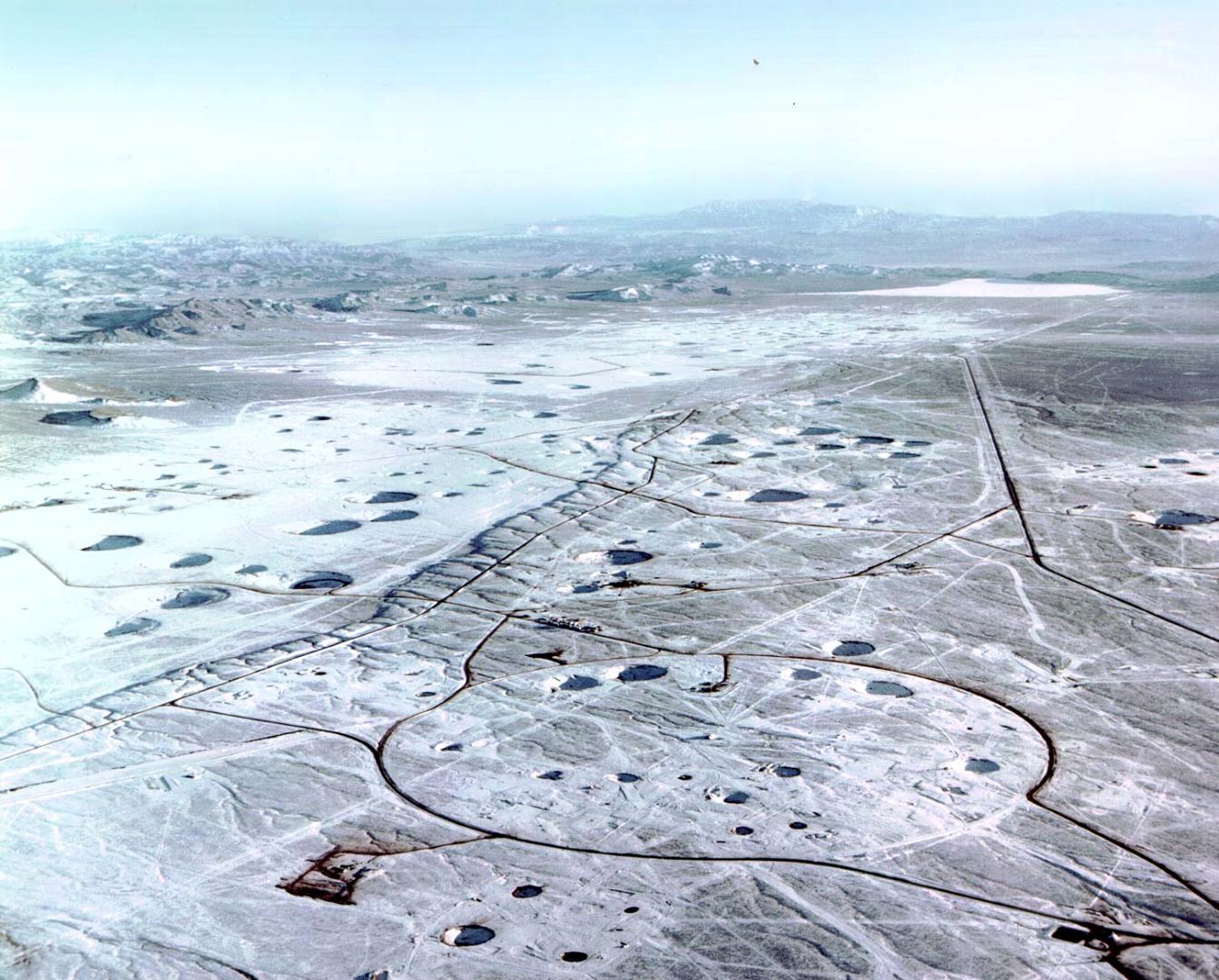
The test ban treaty - the only post war nuclear arms control agreement negotiated between 1994 and 1996 - awaits ratification by eight states – China, Egypt, India, Pakistan, Iran, Israel, North Korea, and the US to become international law. The treaty, signed by 185 countries, bans all nuclear explosions, on land, underground, in the atmosphere and under water. Despite its legal status, only India, Pakistan and North Korea have tested since 1996 when the treaty was first signed, ushering in a moratorium after more than 2,000 nuclear tests.
Why It Matters
Development of a nuclear weapon for the first time without being able to test it is extremely difficult and preventing testing is a brake on making more powerful weapons. Nuclear testing has caused severe damage to the environment and bequeathed a legacy of human ill health.
In 2020 The US Trump administration signalled it was considering resuming testing before changing course. In 1954 Indian Prime Minister Jawarhalal Neru proposed a ‘standstill agreement’ on nuclear testing. There were further efforts in the cold war to halt testing. After the CTBT was first signed US President Bill Clinton declared it “the longest sought, hardest fought prize in arms control history.” Since then more than a billion dollars has been invested in the CTBT’s global monitoring system establishing more than 300 facilities to detect any evidence of a nuclear explosions. The system successfully detected all six North Korean tests.
Further materials:
https://web.archive.org/web/20060228121510/http://www.abc.net.au/news/newsitems/200602/s1577409.htm
http://svaradarajan.blogspot.com/1999/10/test-ban-test-us-rejection-has.html