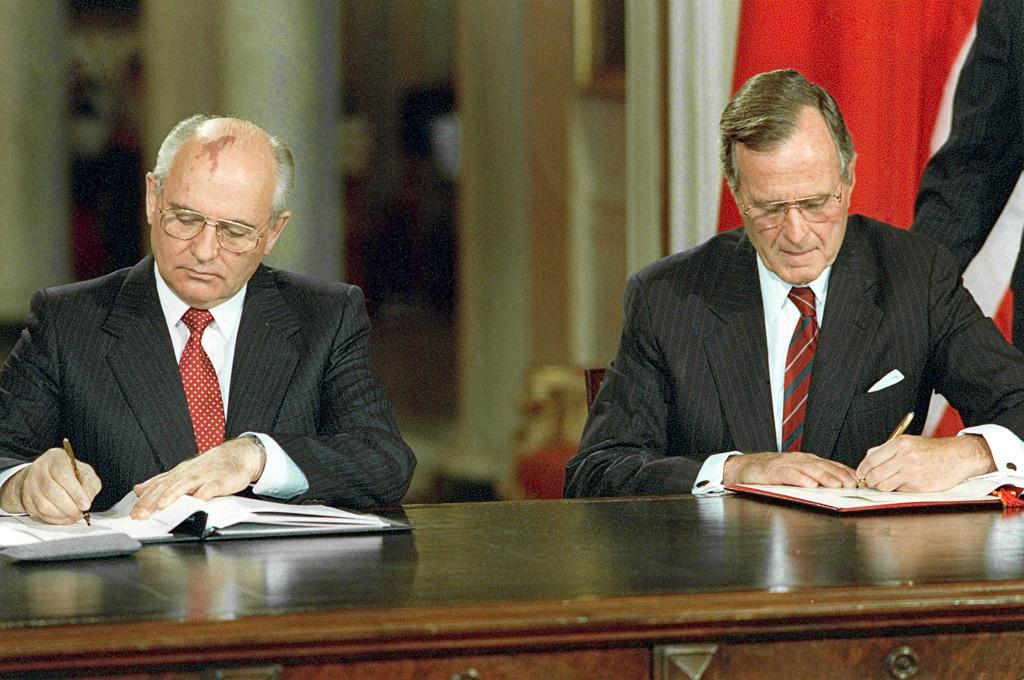
After almost ten years of intensive bargaining, START I was signed on 31 July 1991 by George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev. It was the first treaty on reductions of US and soviet strategic nuclear weapons and entered into force in 1994.
Why It Matters
The treaty provisions obliged the parties to reduce their stockpiles of deployed strategic arsenals to 1,600 delivery vehicles with a cap of 6,000 warheads. Additionally, intrusive verification schemes were introduced, including the continuous exchange of information. The treaty only entered into force in 1994 because the Soviet Union dissolved five months after START I was signed. In 1992 the Lisbon Protocol requiring the newly independent states of Ukraine, Belarus, and Kazakhstan to return their nuclear weapons to Russia also delayed its introduction.
Even though it took the START I agreement three years to enter into force, cooperation in specific areas of the treaty, such as sharing data on strategic weapons and verification, began shortly after its signature, The spirit of cooperation was indicative of the post-Cold War era sentiment and the result of years long negotiations, that continued throughout the treaty’s fifteen year duration. Reductions under the treaty were completed by December 2001. Bilateral arms reductions were intended to continue under the START II treaty which did not enter into force.
Further Materials: