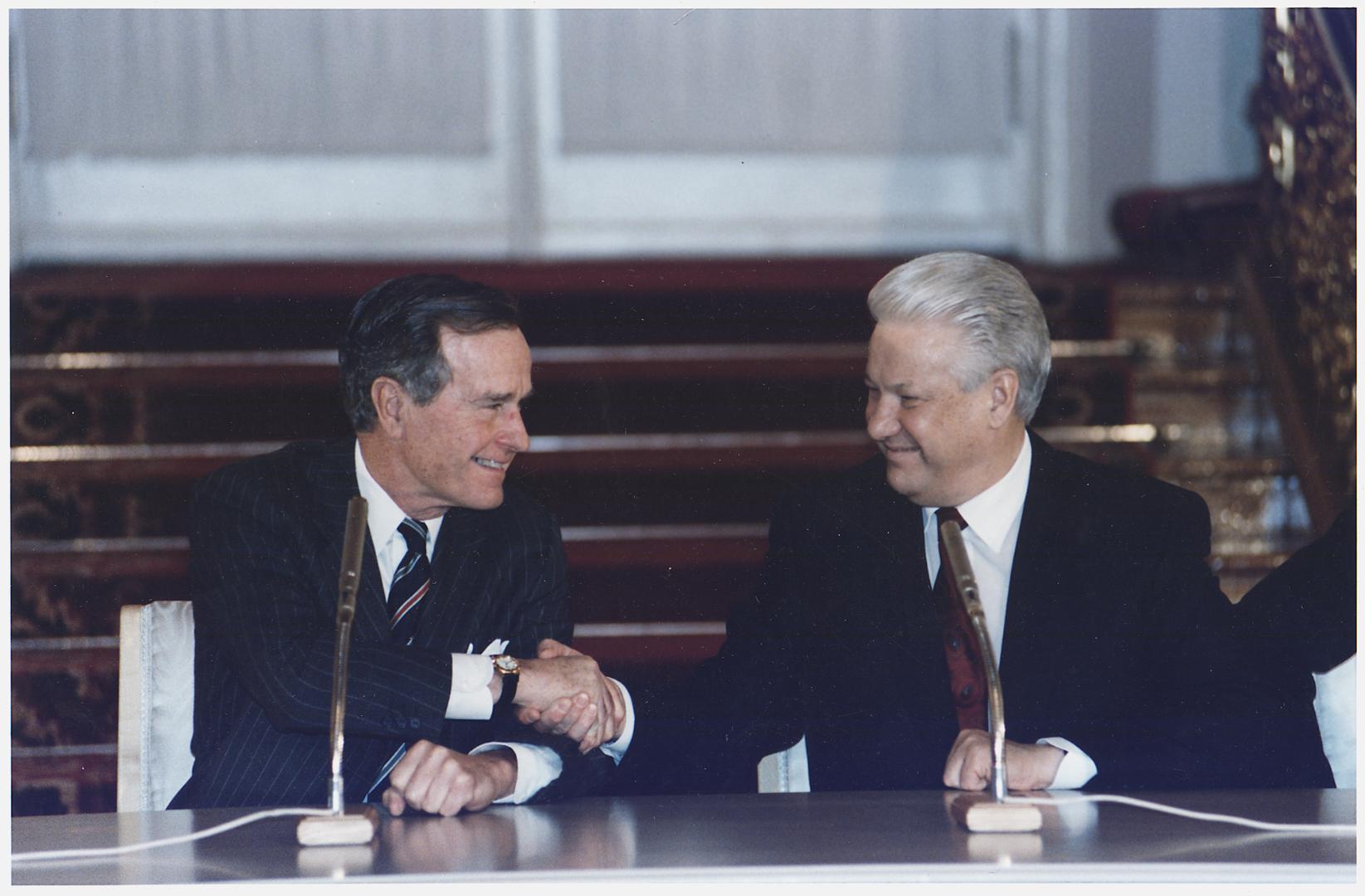
The START II agreement was signed on 3 January 1993, after Presidents George H.W. Bush and Boris Yeltsin had agreed in 1992 to a successor to to START I, while it was not yet in force. START II maintained the spirit of mutual arms reduction carried over from previous negotiations and set out to further reduce the US and Russian stockpiles of strategic nuclear weapons. Although both parties ratified the agreement it did not go into force.
Why It Matters
The START II agreement was intended to be a continuation of START I providing additional provisions for both parties. The number of strategically deployed warheads would be reduced to 3,000-3,500 by December 2007, multiple warhead land based missiles banned, and delivery vehicles destroyed. Further inspections, as well as a Bilateral Implementation Commission (BIC), a dispute settlement body, were to be introduced.
After George H. W. Bush and Boris Yeltsin signed START II in 1993, it was ratified by the US in 1996 and by Russia in 2000. However, the US failed to ratify the 1997 Protocol, a set of political and technical agreements meant to enhance START II, clarify issues of the ABM treaty and increase dialogue. As a direct response to Washington’s withdrawal from the ABM in 2002, Moscow declared it was no longer bound by any of the START II obligations ending its lifespan. While Russia and the US signed the SORT agreement key provisions concerning multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs) were not included.
Further Materials: